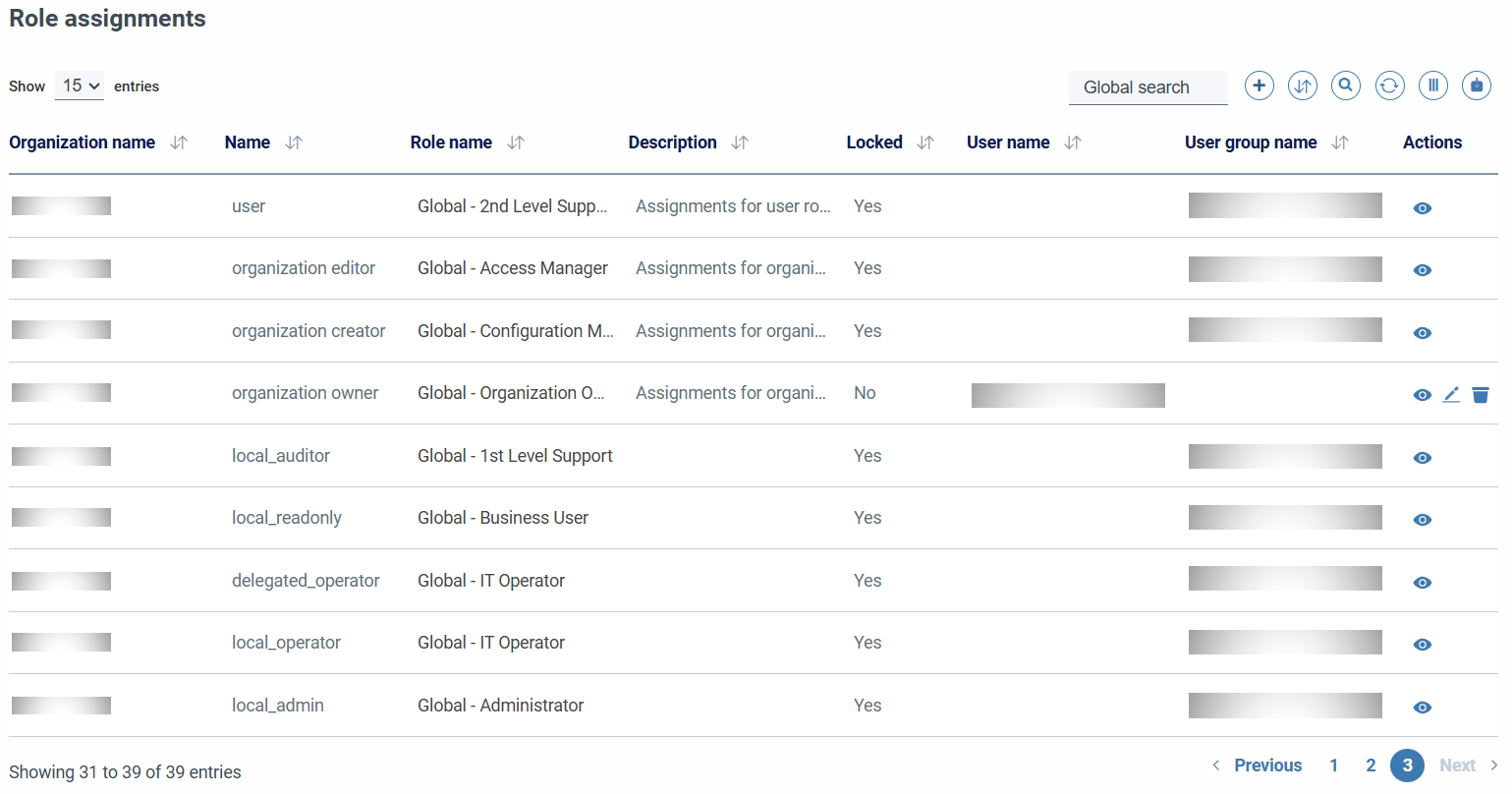
Role assingments
Role assignment¶
The new SSMCM permission system is based on assigning roles to users or groups of users. In this way, greater flexibility and isolation is achieved between the permissions of the different organizations. This system is very similar to the one used in AWS, Azure or Google Cloud.
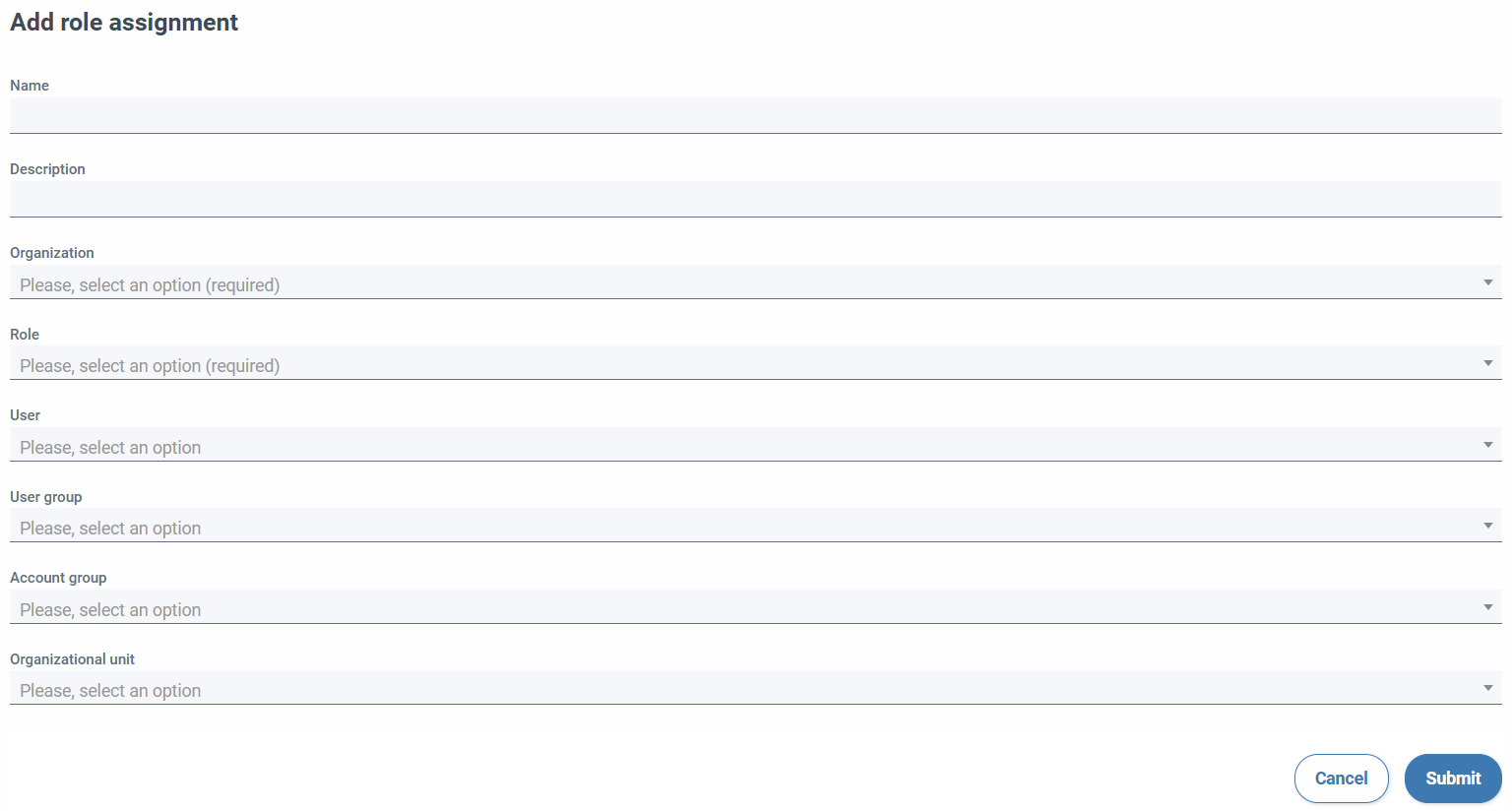
When giving permissions, the following fields must be specified:
- A descriptive name
- An optional description
- The organization being worked on
- The role to assign
- Who is going to be given permissions, which can be an object of one of two types:
- A possible limitation of accounts on which role permissions will apply, based on two types:
- a group of accounts
- Accounts that are under an organizational unit (only applies to AWS accounts)
When creating/editing a role assignment, we must take into account the following:
- It is necessary to specify the organization on which the assignment is applied; We must have permissions on that organization, or that our user has the ability
CAPABILITY_GLOBAL_PERMISSION_MANAGEMENT(global_permission_management). - We can only select a role that is global or belongs to the same organization that we have selected.
- When selecting a user or a group of users on which the role is applied, the selector will automatically search for the users or groups of the organizations to which we have access; If we want to add users or groups from other organizations, it is also possible, but we must indicate the exact name of the group, or the name / user ID / email exact of the user.
- For roles that have permissions on accounts or on account-related objects, we may restrict which accounts are accessed by selecting an account group or organizational unit (AWS accounts only).
A role assignment might be locked (locked). In this case, this assignment is defined by the application administrators and cannot be edited or modified. This can happen, for example, when administration and operation has been delegated to the specific team, so that multiple locked items with permissions to groups in the designated organization would appear in the role assignment list.
A role assignment can also appear blocked when they are elementary assignments, that is, those that provide the minimum functionality for the application to work; for example, those for the organization's management groups.
The resulting permissions for a specific user can be consulted from the User → Permissions.